 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
|
|
|
|
Steering Encyclopedia by Unisteer
|
|
|
|
What is Ackermann Steering?
System of double-pivot steering in which two steered wheels pivot about a vertical axis and are steered by linked steering arms. The system was devised by Lankensperger but takes its name from the patent agent Ackermann.
|
|
|
What are AN Fittings?
The AN thread is a particular type of fitting used to connect flexible hoses and rigid metal tubing that carry fluid. The term "AN" is a US military-derived specification stemming from a joint standard agreed upon by the Army and Navy, hence "AN", but some documents point to a Air Force/Navy agreement. The AN flared hydraulic fittings are widely used throughout the performance & aftermarket automotive industry.
AN fittings are a flare fitting, using 37� flared tubing to form a metal-metal seal. They are similar to other 37� flared fittings, such as JIC fittings, which is their industrial variant. The two are interchangeable in theory, though this is typically not recommended to mix them due to the exacting specifications and demands of the aerospace industry. The differences between them relate to thread class (how tight a fit the threads are) and the metals used.
AN sizes range from -2 (dash two) to -32 in irregular steps, with each step equating to the OD (outside diameter) of the tubing in 1/16" increments. Therefore, a -8 AN size would be equal to 8/16" (8 x 1/16") which is actually 1/2" OD tube. However, this system does not specify the ID (inside diameter) of the tubing because the tube wall can vary in thickness from manufacturer to manufacturer. For example, the inside diameter of an Earl's -6 AN hose end is nearly as large as the inside diameter of some other manufacturers' -8 AN hose ends. Each AN size also uses its own standard thread size according to the scale of the fitting.
|
|
|
What is Ball Center?
This is the dimension between the pivot points of a steering system: the arc that the inner and outer tie rods move through should be the same as the arc that the control arms move through. The center of the pivot on the driver side to the center of the pivot on the passenger side gives the ball center dimension It is vital that the ball center match the steering geometry of the front suspension.
|
|
|
|
What is Bump Steer?
Bump Steer is the condition that occurs when your wheels have a tow change when they leave the pavement(such as hitting a bump). If a rack and pinion has the inner tie rods that are spaced wider apart than the stock configuration excessive bump steer can and will occur.
There is an urban legend of sorts concerning what bump-steer is. Some guys believe that bump steer is the vibration or shaking that you feel when you drive.
The easiest way to verify if a rack and pinion kit will or will not create Bump Steer is to measure the inner tie-rod sockets on a rack and pinion kit to that of the inner tie rods on the factory center link.
We spend a great deal of time and effort designing and manufacturing our rack and pinion kits to assure that work with the factory front-end parts. It would be much easier and cheaper for us to simply use an off-the-shelf gear and shorten
|
|
|
|
What is the Camber?
Looking at a vehicle from the front, the Camber is the angle that the tires lean at vertically. Positive Camber means that the top of the tire is angled away from the vehicle. Negative Camber means that the top of the tire is angled towards the vehicle.
|
|
|
|
What is Caster ?
Looking at a vehicle from the side, Caster is the angle of the steering axis line relative to vertical. Positive Caster means the top of the steering axis line is angled towards the rear of the vehicle. Negative Caster means that the top of the steering axis line is angled towards the front of the vehicle.
|
|
|
|
What is the Center Link?
In a conventional steering system, the center link attaches all parts of the steering system, pitman arm, two inner tie-rods, and idler arm. The distance between the two holes for the two inner tie-rods gives the ball center dimension for that steering system. SEE DIAGRAM BELOW
|
|
|
|
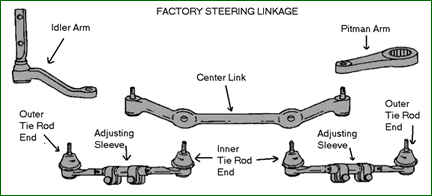 |
|
|
|
What is a Drag Link?
A Drag Link functions in conjunction with most solid axle vehicles, connecting the driver side and passenger side wheels. When a steering box or an end take off rack combined with a steering arm are used, they steer one wheel, the drag link connects this wheel with the opposite wheel so that both are used.
|
|
|
|
What is an End Take Off Rack?
A Rack & Pinion that steers off one side only, in conjunction with a drag link, duplicating the motion of a steering box on solid axle vehicles.
|
|
|
|
What is Independent Front Suspension?
Front Suspension of a vehicle where the front two wheels travel independently of each other.
|
|
|
|
What is the Inner End?
Also commonly referred to as the ball joint, this ball and socket joint is the pivot point or points of a Rack & Pinion, this is where the rack and pinion will pivot for travel. It is usually located under the rubber bellow (boot) of the rack & pinion.
|
|
|
|
What is the Inner Tie Rod End (Inner Ball Joint)?
For stock steering, or steering systems utilizing a steering box, this is the inner pivot point or points, of that steering system.
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
|
What is the Outer Tie Rod End (Outer Ball Joint)?
This is the outside pivot point of the majority of steering systems, sometimes it is substituted with a Heim joint. The outer tie rod end is attached to the steering arms on each wheel.
|
|
|
|
What is Power Steering Pump Pressure & Flow?
The principle of power steering pressure and flow is that it must match the steering system you have. Any old power steering pump will not necessarily work with your steering system. A Rack & Pinion requires a lower pressure, lower flow pump, as opposed to power steering boxes, which require a higher pressure, higher flow pump. A typical problem is that one experiences over-steer, or super sensitive steering with a power rack & pinion. The rack and pinion is not bad, it is the pump, there is too much pressure and flow. Pressure reducing valves are not an effective way to fix the pump, these valves do not reduce the flow at all. A different pump is required, keeping in mind most pumps look exactly alike but there are many different internal configurations even with in the same model such as with the GM Type II pump.
|
|
|
|
What is the Pitman Arm?
The pitman arm is a splined arm that transfers the rotational force of the steering box output shaft as a direct result of the steering effort from the driver and acts like a lever converting torque from the steering gear to mechanical force for movement of the steering linkage.
A pitman arm is used on vehicles with parallelogram steering. This steering configuration was and is used on virtually all rear-wheel-drive vehicles and most light-duty trucks.
The pitman arm connects the steering gear box and the steering linkage via a threaded bearing stud with a conical seat. The lower part of the threaded bearing stud is covered with a protective dust boot that prevents dirt entry into the bearing and seat. The upper part of the bearing stud connects to the center link of the steering linkage.
|
|
|
|
What are Power Steering Rack & Pinion Pressure and Return Lines?
A Power Steering Rack & Pinion has 4 ports usually on the pinion housing; two of these ports run the lines to the rack tube on a Rack & Pinion, the other two ports go to the power steering pump. The pressure port is the smaller diameter port, and return line is the larger diameter port. If the ports are the same size or you can not tell by this method, then look at the location of the ports. One port will be located in a position on an axis that horizontally (or perpendicularly)(relative to the pinion) splits the two ports that run the lines to the steering gear. That port is the pressure port, the other is the return port.
|
|
|
|
What is a Rack & Pinion?
A Steering Gear system in which a pinion on the end of the steering shaft engages with a horizontal rack, the ends of which are coupled to the steering arms by tie rods.
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
|
What is Rack Travel?
Applied to steering, this term refers to the distance that the rack moves in a horizontal plane when the pinion is turned. Specifically, it correlates to the amount of area in which the teeth are cut on the rack. The rack can travel only as far as there are teeth cut on the rack, keep in mind that the rack does not have to travel that full distance. .
|
|
|
|
What is Rear Steer?
A term used to describe a steering system that is behind the axle of the vehicle.
|
|
|
|
What is Recirculating Ball Steering?
The recirculating-ball steering gear contains a worm gear. You can image the gear in two parts. The first part is a block of metal with a threaded hole in it. This block has gear teeth cut into the outside of it, which engage a gear that moves the pitman arm. The steering wheel connects to a threaded rod, similar to a bolt, that sticks into the hole in the block. When the steering wheel turns, it turns the bolt. Instead of twisting further into the block the way a regular bolt would, this bolt is held fixed so that when it spins, it moves the block, which moves the gear that turns the wheels.
Instead of the bolt directly engaging the threads in the block, all of the threads are filled with ball bearings that recirculate through the gear as it turns. The balls actually serve two purposes: First, they reduce friction and wear in the gear. Second, they reduce slop in the gear. Slop is felt when you change the direction of the steering wheel. Without the balls in the steering gear, the teeth would come out of contact with each other for a moment, making the steering wheel feel loose.
Power steering in a recirculating-ball system works similarly to a rack-and-pinion systems. Steering assist is provided by supplying higher-pressure fluid to one side of the block.
|
|